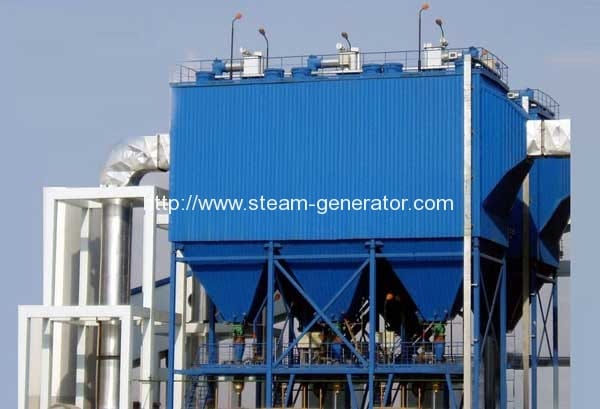
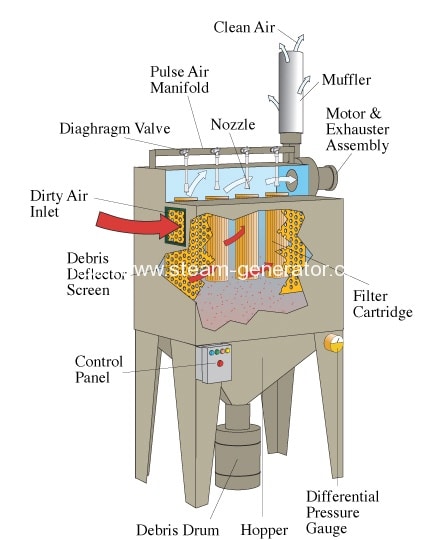
A dust collector is a system used to enhance the quality of air released from industrial and commercial processes by collecting dust and other impurities from air or gas. Designed to handle high-volume
dust loads, a dust collector system consists of a blower, dust filter, a
filter-cleaning system, and a dust receptacle or dust removal system.
It is distinguished from air cleaners, which use disposable filters to remove dust.
A baghouse (BH, B/H) or fabric filter (FF) is an air pollution
control device that removes particulates out of air or gas released
from commercial processes or combustion for electricity generation. Power plants, steel mills, pharmaceutical producers, food
manufacturers, chemical producers and other industrial companies often
use baghouses to control emission of air pollutants. Baghouses came into widespread use in the late 1970s after the
invention of high-temperature fabrics (for use in the filter media)
capable of withstanding temperatures over 350 °F.
Unlike electrostatic precipitators,
where performance may vary significantly depending on process and
electrical conditions, functioning baghouses typically have a
particulate collection efficiency of 99% or better, even when particle
size is very small.